Printing technology
Printing
technology
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, applies materials such as polymers or metals layer by layer to create individual parts or entire assemblies. The wide variety of technologies and materials available makes it possible to produce thin wall thicknesses as well as complex geometric shapes and fine to transparent surfaces. Rapid prototyping is used to produce prototypes quickly, significantly reducing the time it takes to manufacture various assemblies.
The key technologies
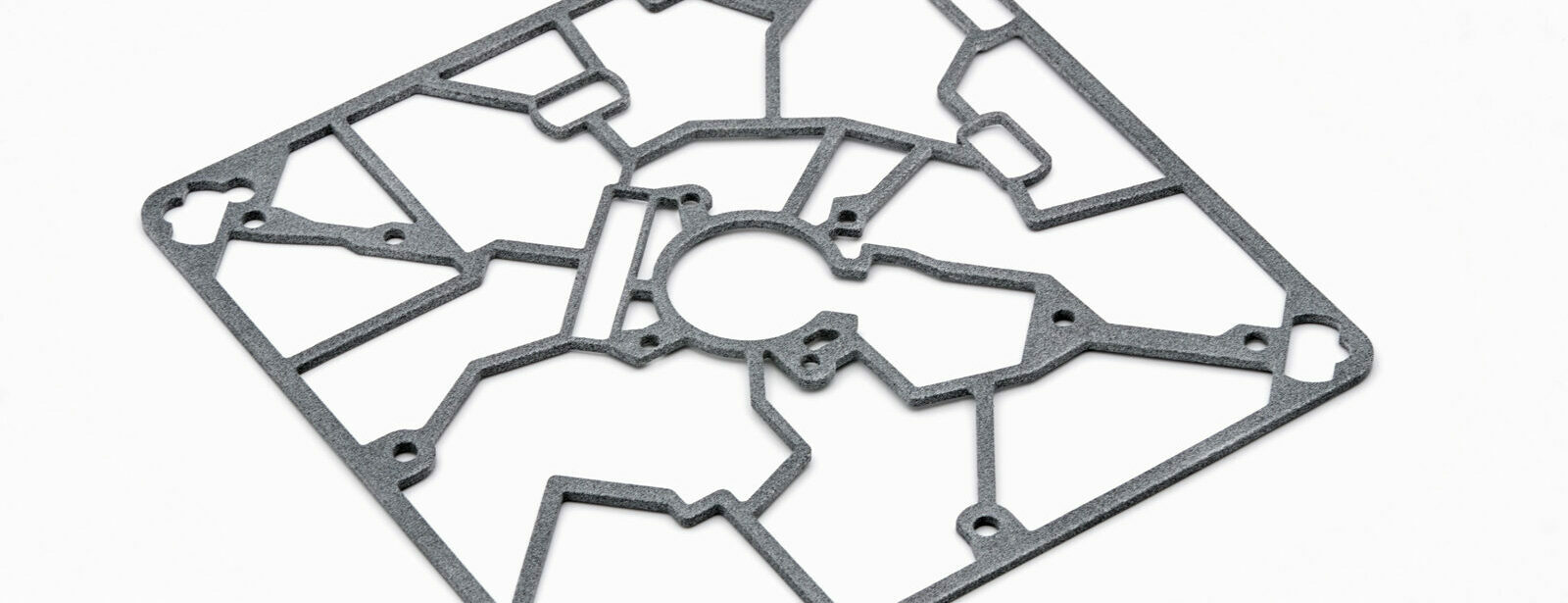
SLS – Selective laser sintering
This process, which is the most frequently used in the professional sector, is suitable for a wide variety of plastics – including glass-fibre reinforced and flexible rubber-like plastics. In the SLS process, the powdery raw material is cured layer by layer with a laser beam. No elaborate supporting structures are required, making the process very cost-effective.
MJF – Multi-jet fusion
Only PA 12 (polyamide) in powder form is used in this process. A binding agent is cured with infrared. Very solid parts and a high surface quality can be achieved with the MJF process, resulting in products of a similar standard to those produced using the SLS method.
FDM – Fused deposition modelling
In this traditional process, the plastic filament is applied with an extrusion nozzle. ABS, PLA, ASA and high-performance plastics such as PPSU can be processed using this method.
MJM – Multi-jet modelling
With multi-jet modelling, liquid plastics are applied and cured by UV light. This process allows very fine surfaces and transparent models to be produced.
SLM – Selective laser melting
This process is similar to SLS, but is specifically for metals. In selective laser melting, metal powder is melted layer by layer with a laser. This process is a cost-effective and quick alternative to traditional metal castings. Aluminium and steel alloys can be processed.